cEX <<
Previous Next >> 練習1
課程1
2
1.
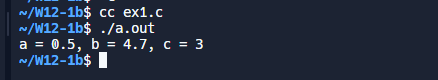
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float a = 0.5;
double b = 1.2;
int c = 3;
b = b + a + c;
/* 输出 a, b, c 到屏幕 */
printf("a = %3.1f, b = %3.1f, c = %d\n", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
2.
/* ====================
字元範例 1
==================== */
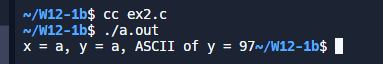
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char x, y;
x = 'a';
y = (char)97;
/* 輸出 x, y, x, 最後一個是以 ASCII 值顯示 y */
printf("x = %c, y = %c, ASCII of y = %d", x, y, y);
return 0;
}
3.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 64;
int b = 0x40; // 以十六进制表示
long c = 64L;
// 打印变量的值
printf("%d, %d, %ld", a, b, c);
return 0;
}

4.
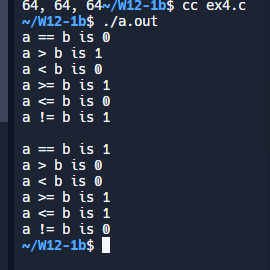
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 5;
// 第一组比较
printf("a == b is %d\n", a == b);
printf("a > b is %d\n", a > b);
printf("a < b is %d\n", a < b);
printf("a >= b is %d\n", a >= b);
printf("a <= b is %d\n", a <= b);
printf("a != b is %d\n", a != b);
printf("\n");
// 修改 b 的值
b = 10;
// 第二组比较
printf("a == b is %d\n", a == b);
printf("a > b is %d\n", a > b);
printf("a < b is %d\n", a < b);
printf("a >= b is %d\n", a >= b);
printf("a <= b is %d\n", a <= b);
printf("a != b is %d\n", a != b);
return 0;
}
5.
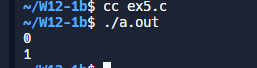
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a;
// 第一次输出
a = 3;
printf("%d\n", !a); // 逻辑非运算,a为真,所以输出0
// 第二次输出
a = 0;
printf("%d\n", !a); // 逻辑非运算,a为假,所以输出1
}
6.
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
char a;
// 使用 %zu 格式说明符输出 size_t 类型
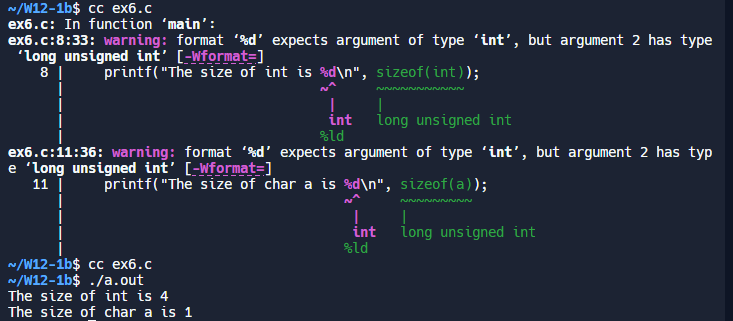
printf("The size of int is %zu\n", sizeof(int));
// 使用 %zu 格式说明符输出 size_t 类型
printf("The size of char a is %zu\n", sizeof(a));
}
7.
#include <stdio.h>
/* ====================
计算长方形面积, 需传入长与宽.
==================== */
int rect(int x, int y)
{
int result;
result = x * y;
return result; /* 返回 result */
}
/* ====================
主函数
==================== */
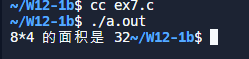
int main()
{
int x = 8, y = 4;
int a;
a = rect(x, y);
printf("8*4 的面积是 %d", a);
return 0;
}
8.
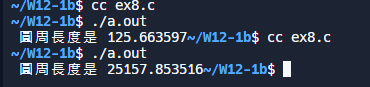
#include <stdio.h>
float circle( int r ); /* 宣告 circle 的 prototype */
void main()
{
float answer;
answer = circle(8);
printf( " 圓周長度是 %f", answer );
}
/* ====================
circle 函數, 計算 circle 的圓周長
==================== */
float circle( int r )
{
float result;
result = 3.14159 * (double)1001 * r;
return ( result );
}
9,
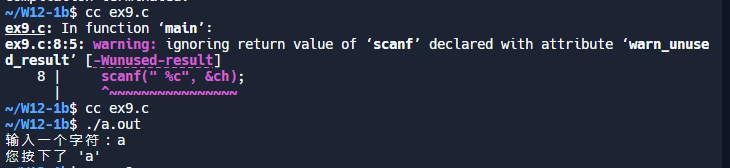
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ch;
printf("输入一个字符:");
// 检查 scanf 的返回值,确保成功读取一个字符
if (scanf(" %c", &ch) != 1) {
printf("读取字符失败\n");
return 1; // 或者采取其他错误处理措施
}
if (ch == 'a') {
printf("您按下了 'a'\n");
}
return 0;
}
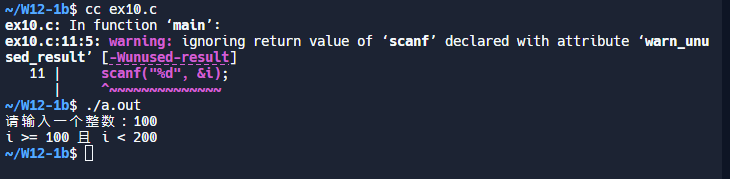
10.
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
// 提示用户输入一个整数
printf("100:");
// 读取用户输入的整数
scanf("%d", &i);
// 判断输入的整数,并输出相应的消息
if (i < 100)
{
printf("i < 100\n");
}
else
{
if ((i >= 100) && (i < 200))
{
printf("i >= 100 且 i < 200\n");
}
else
{
printf("i >= 200\n");
}
}
}
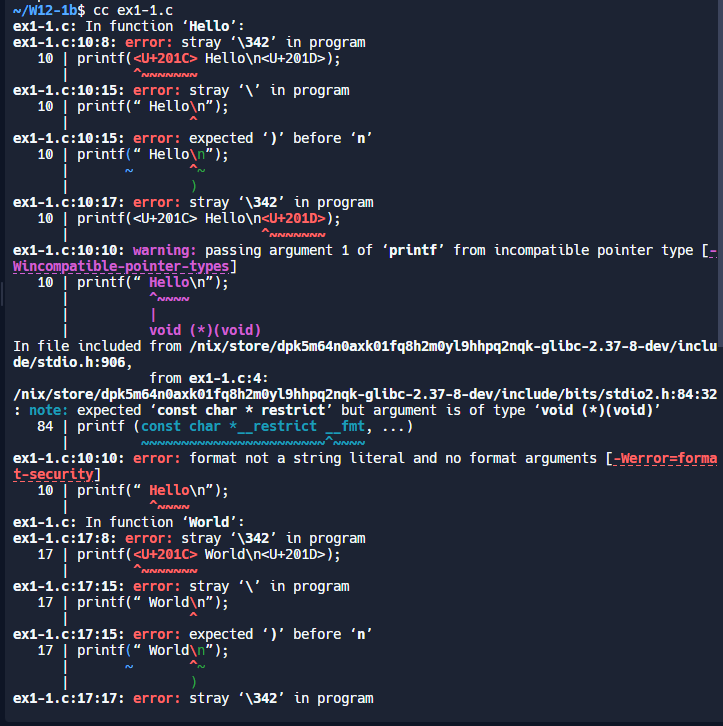
1.1
/* =========================
function pointer 2
========================= */
#include <stdio.h>
/* ====================
say “Hello”.
==================== */
void Hello(void)
{
printf(“ Hello\n”);
}
/* ====================
say “World”.
==================== */
void World(void)
{
printf(“ World\n”);
}
/* ====================
main function.
==================== */
int main()
{
void (*func[3])(void); /* 宣告一個 function pointer array */
int i = 0 ;
func[0] = Hello; /* 建立 Jumping table */
func[1] = World;
while(1)
{
printf(“Input a number between 0 and 1 : ”);
scanf( “%d”,&i );
/* 若 I 大於等於 2 或是小於 0 則離開 loop */
if( (i >= 2)||(i < 0) )
break;
else
func[ i ]( ); /* 執行! */
}
return 0;
}
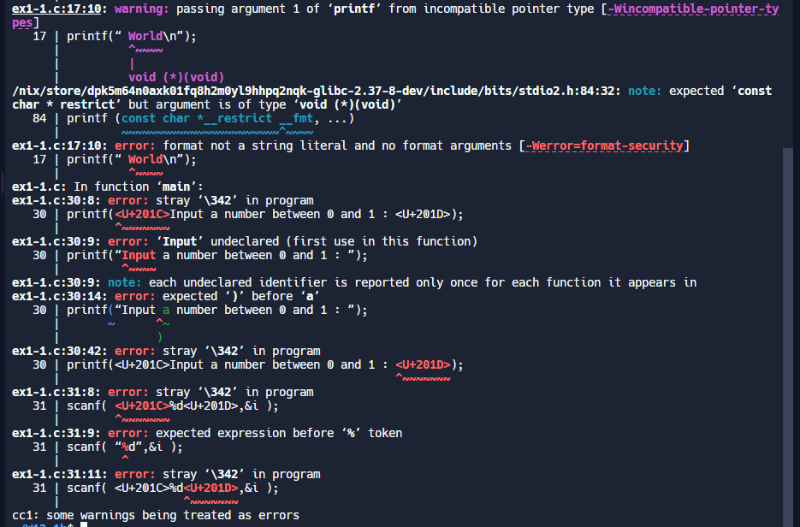
1.2
#include <stdio.h>
/* ====================
say “Hello”.
==================== */
void Hello(void)
{
printf("Hello\n");
}
/* ====================
say “World”.
==================== */
void World(void)
{
printf("World\n");
}
/* ====================
main function.
==================== */
int main()
{
void (*func[3])(void); /* 声明一个函数指针数组 */
int i = 0;
func[0] = Hello; /* 建立 Jumping table */
func[1] = World;
while (1)
{
printf("Input a number between 0 and 1: ");
scanf("%d", &i);
/* 如果 i 大于等于 2 或小于 0 则退出循环 */
if (i >= 2 || i < 0)
break;
else
func[i](); /* 执行函数 */
}
return 0;
}
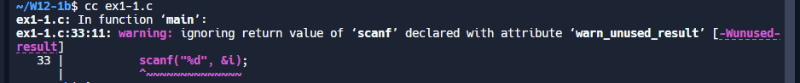
1.3
#include <stdio.h>
/* ====================
say “Hello”.
==================== */
void Hello(void)
{
printf("Hello\n");
}
/* ====================
say “World”.
==================== */
void World(void)
{
printf("World\n");
}
/* ====================
main function.
==================== */
int main()
{
void (*func[3])(void); /* 声明一个函数指针数组 */
int i = 0;
func[0] = Hello; /* 建立 Jumping table */
func[1] = World;
while (1)
{
printf("Input a number between 0 and 1: ");
// 检查 scanf 的返回值,确保成功读取一个整数
if (scanf("%d", &i) != 1)
{
printf("无效输入,请输入一个整数。\n");
break;
}
/* 如果 i 大于等于 2 或小于 0 则退出循环 */
if (i >= 2 || i < 0)
break;
else
func[i](); /* 执行函数 */
}
return 0;
}

2.1
/* ====================
pointer to pointer – 1.
==================== */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *Hello = “Hello”;
char *World = “World”;
char *GoodBye = “Good Bye”;
char *StrArray[3];
char **Str;
int i;
Str = StrArray;
StrArray[0] = Hello;
StrArray[1] = World;
StrArray[2] = GoodBye;
for( i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
printf(“%s”, StrArray[ i ] );
}
for( i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
printf(“%s”, *Str );
Str++;
}
retur
2.2
/* ====================
pointer to pointer – 1.
==================== */
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char *Hello = "Hello";
char *World = "World";
char *GoodBye = "Good Bye";
char *StrArray[3];
char **Str;
int i;
Str = StrArray;
StrArray[0] = Hello;
StrArray[1] = World;
StrArray[2] = GoodBye;
// Print strings using array indexing
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("%s ", StrArray[i]);
}
// Print strings using pointer arithmetic
Str = StrArray; // Reset the pointer to the beginning
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("%s ", *Str);
Str++;
}
return 0;
}
我的圖片不知道為甚麼不能傳所以我用打字說明
先打cc ex.2-1.c再來打./a.out Hello World Good Bye Hello World Good Bye
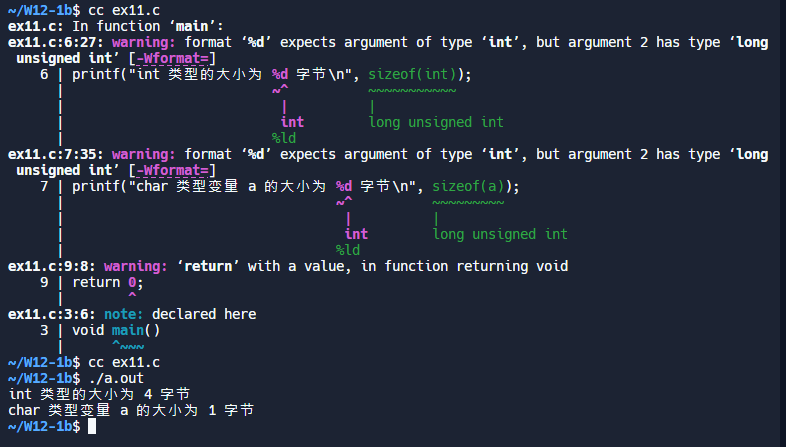
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("int 类型的大小为 %zu 字节\n", sizeof(int));
char a;
printf("char 类型变量 a 的大小为 %zu 字节\n", sizeof(a));
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float this_is_a_number1, this_is_a_number2;
int scanf_result; // Dummy variable to capture scanf's return value
/* 读取输入的浮点数 */
scanf_result = scanf("%f", &this_is_a_number1);
/* 读取输入的浮点数 */
scanf_result = scanf("%f", &this_is_a_number2);
/* Your code here */
return 0;
}

cEX <<
Previous Next >> 練習1